Cold heading, or cold forming, is a production process used to create fasteners and other specialty parts quicker and more effectively than other manufacturing techniques. This process creates various headpiece tools, including screws, shoulders, and fasteners. Compared to screw machining, cold heading is superior because there is less scrap produced through this process. Compared to screw machining, this process results in significant savings on raw materials. Cold heading also raises the performance of the product. Cold heading reorganizes the grain structure, enhancing shear strength performance and avoiding disruptions to grain flow. Read More…
At Chicago Nut & Bolt, we specialize in manufacturing high-quality cold headed parts tailored to meet the most demanding industrial specifications. With decades of experience in fastener production, we have built a reputation for delivering precision-engineered components that perform reliably in critical applications.

Global manufacturer Stalcop specializes in the manufacturing of cold headed parts. Stalcop can meet your needs with specialty solutions, combining processes with secondary operations such as CNC machining and assembly. With over 100 years combined experience, count Stalcop for quality and lower prices! Stalcop serves its customers by offering products and services that are consistent and timely.

At Precision Metal Components, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance cold headed parts that deliver superior strength, precision, and reliability across demanding industries. Through advanced cold heading technology, we shape metal with exacting accuracy while minimizing material waste and improving structural integrity.

Here at NSK Industries, Inc. we are a turnkey manufacturing which means we will supply your cold forming needs with a short amount of lead time. Our company manages four facilities and we strive to be an unsurpassed supplier. We have the background and production lines that can get your projects done regardless of complexity. We are eager to adhere to your specifications. Please visit our website ...

More Cold Headed Fastener Manufacturers

Cold heading results in higher quality over other manufacturing processes since the smoothness and dimensions of a die are directly transferred to a product’s surface. This quality eliminates the need for secondary finishing procedures associated with other manufacturing techniques and, as a result, costs associated with parts, labor, inspection, tolerance issues, and purchases are all reduced.
Cold heading creates the potential to reduce multi-part assemblies to single-part assemblies. Cold heading also creates tight tolerance consistency throughout the manufacture of an item. Therefore, cold heading can be used as a combination of primary and secondary machining to achieve part configurations where a tighter tolerance, above and beyond what is typically required, may be needed.
Cold-Headed Fastener Production
Cold heading is a multi-step production process that creates metal objects while they are still at room temperature. Cold heading uses a series of hammers and dies to form metal without heating it. Cold heading begins, however, with a drawing machine which pulls a thick coil of wire through a blank. The material is compressed to the desired diameter by the drawing machine. The blank is struck inside the cold heading machine between a punch block and a die, forcing the material into the die and resulting in the desired shape.
Cold-Headed Fastener Manufacturing Processes
There are the two fundamental processes utilized in cold-headed manufacturing, upsets and extrusion. These techniques involve applying sufficient pressure to cause a material to fill a void inside a die. Each die is designed appropriately to ensure the proper amount of material movement during the process.
Cold Heading Upsets
Upsets are currently the most widely utilized and fundamental cold-heading technique. An upset results from decreasing a slug's height while increasing its starting diameter. This method is frequently employed to construct a part's head, and depending on the upset position and shape, it may be formed with open tooling, between tooling, or enclosed tooling. In addition, upsets are used as a means to form integral components featuring various heads and diameters. Additional upsets with intricate arrangements may also be included at various stages of a part's development.
Extrusion
Extrusion is another popular cold-heading method. Extrusions can be classified into two categories: forward extrusion and backward extrusion. Forward extrusions reduce the material's width and length by forcing it through an aperture of a lower diameter. Compression is produced by forward extrusion because the cavity of the two dies is smaller than the diameter of the wire. The starting material may be completely or partially contained in the tooling before this extrusion starts.

A hole or cavity is made with backward extrusion by forcing metal through a punch in the opposite direction. Backward extrusions urge the material inside a die or punch insert to flow around a sharp punch or pin. In most cases, backward extrusion is utilized to create a hole or cavity inside a part.
Cold-Headed Fasteners Applications
Cold heading was traditionally used to create pieces like simple fasteners. Due to continual technical advancements, cold heading can now be used to manufacture highly-specialized fasteners and specialty components. These fasteners include specialist bolts, fasteners used in the production of automobiles, and fasteners used in electronics.
Types of Cold-Headed Fasteners
- Custom Bolts
- Weld Bolts/Screws
- Indented Hex Bolts/Screws
- Screws Shoulder Bolts/Screws
- Collar Bolts/Screws
- Isolator Bolts
- Valve Cover Bolts
- Screws


Advantages of Cold-Headed Forming
- Items are created with tight tolerances leading to greater precision.
- Fasteners are produced at high production rates.
- Cold-headed forming allows for a large volume of capacity.
- Cold-heading forming results in a reduced waste of raw materials.
- Cold-headed forming results in enhanced physical characteristics for the items produced.
- Cold-headed forming results in cost savings when compared to machining.
- Cold-headed forming allows for the capability to produce fasteners with a wide range of diameters.
- A customer's demands can be followed while creating both standard and non-standard configurations.
- Typically, secondary procedures are not required to finish fasteners created through cold-headed forming.
Disadvantages of Cold-Headed Fasteners
Despite the advantages provided for fasteners created through cold-headed forming, there are some disadvantages to be made aware of. Pieces must be formed with more force with cold-headed forming due to the absence of heat. Although dies may be less expensive, the necessary equipment required to produce parts is larger and more expensive.
The parts must also be thicker than in machining because hammers can only squeeze so much metal into a given place. Some materials cannot be utilized in a cold-heading machine, while harder metals may take repeated hits to fill a die. Cold heading machines cannot do rolling, stamping, or bending operations. Therefore, more complex parts will require different processes than cold-headed forming.
Choosing the Correct Cold Headed Fasteners Manufacturer
To make sure you have the most beneficial outcome when purchasing Cold Headed Fasteners from a Cold Headed Fasteners Supplier, it is important to compare at least 4 Suppliers using our Cold Headed Fasteners directory. Each Cold Headed Fasteners Manufacturer has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each Cold Headed Fasteners company website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple Cold Headed Fasteners companies with the same quote.







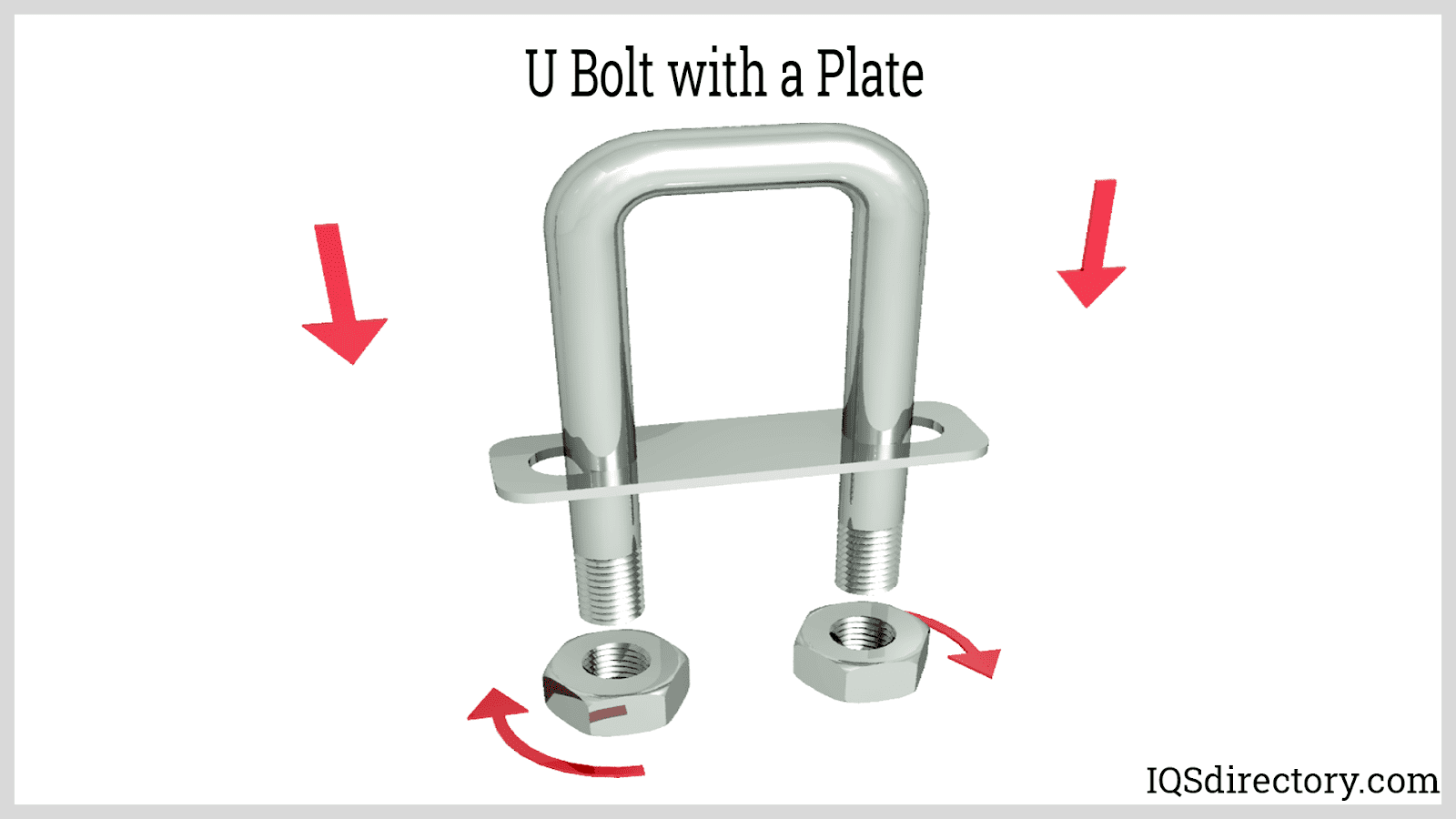

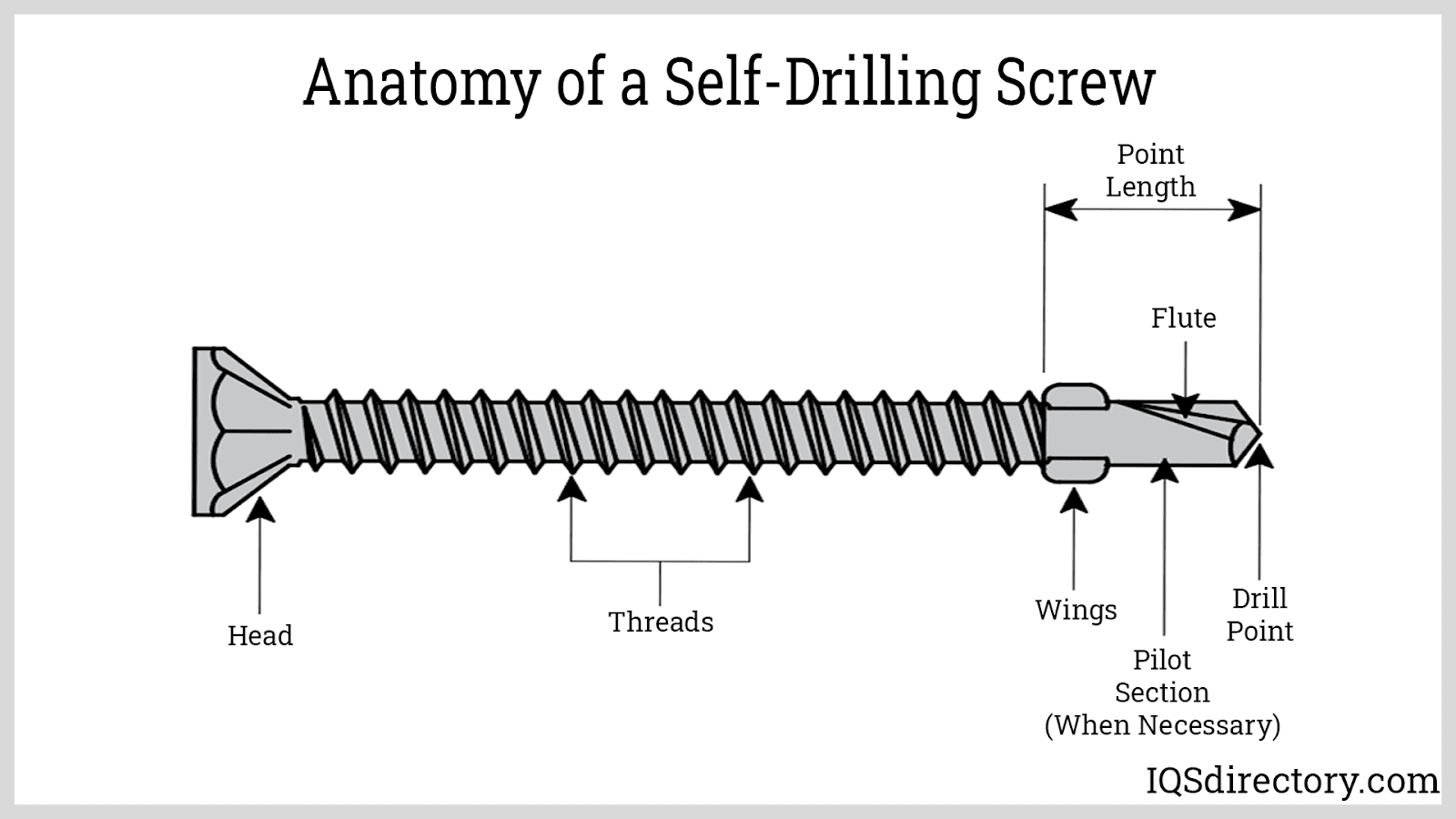
 Cold Headed Parts
Cold Headed Parts Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Metal Spinning
Metal Spinning Powdered Metal Parts
Powdered Metal Parts Roll Forming
Roll Forming Springs
Springs Wire Forms
Wire Forms Wire Mesh
Wire Mesh Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services